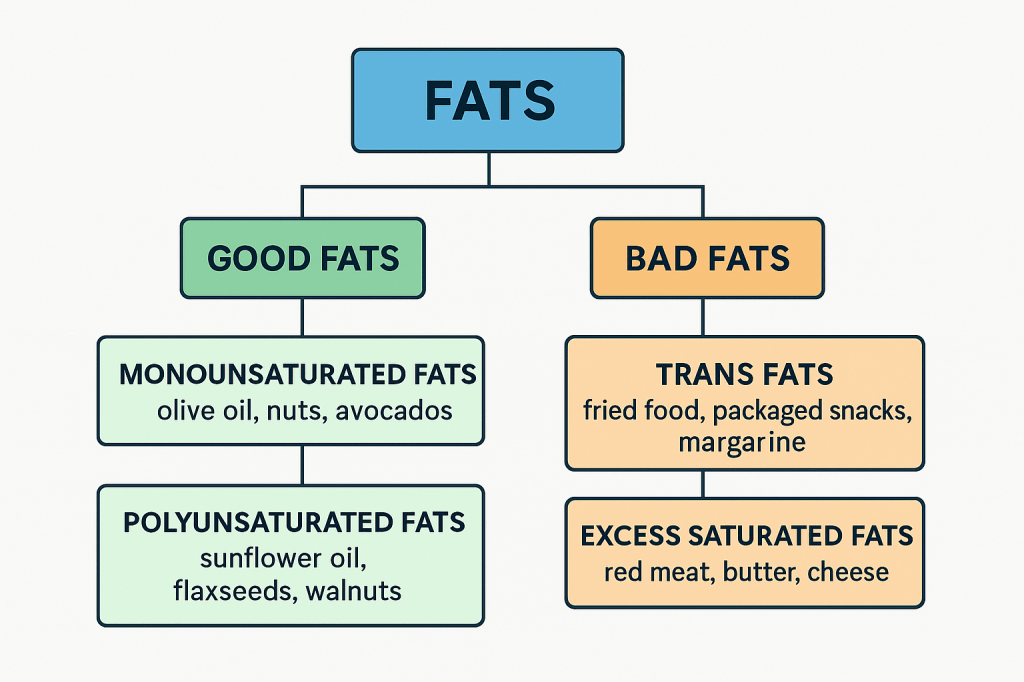
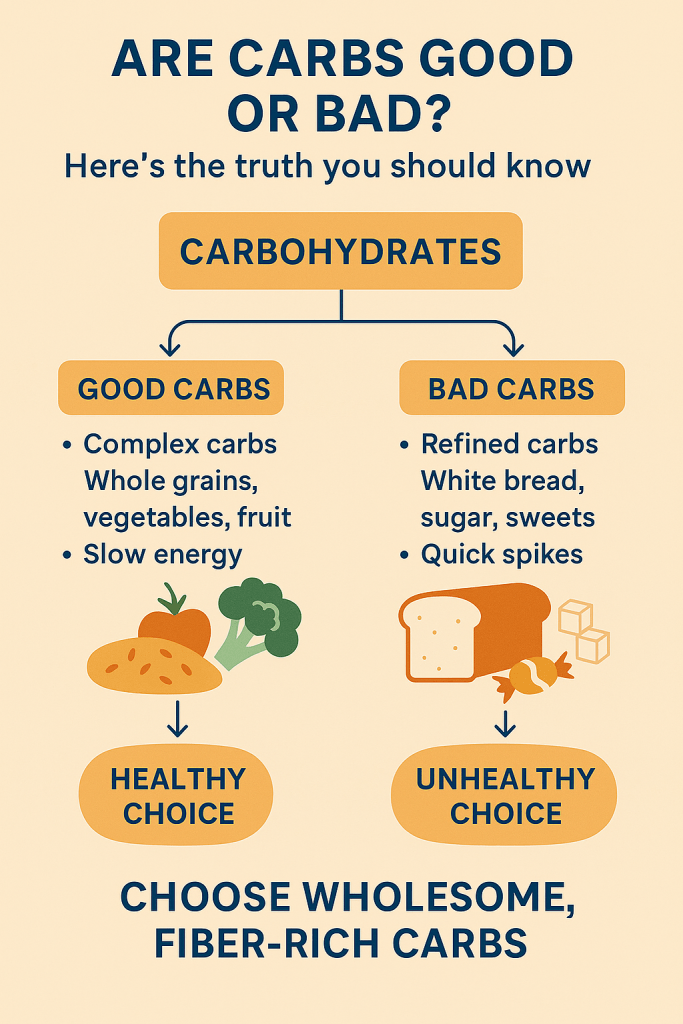
When we think about eating healthy, we often focus on carbs, proteins, and fats. But there’s a group of tiny nutrients that quietly do some of the biggest jobs in our body — micronutrients.
Let’s break them down step by step.
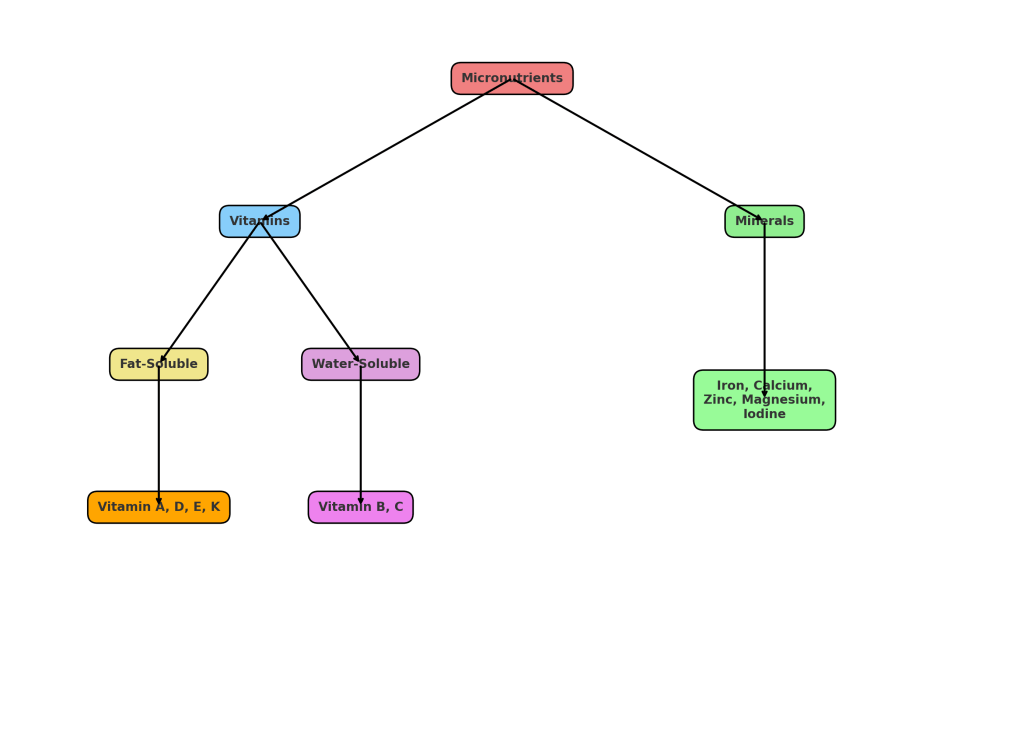
What Are Micronutrients?
Micronutrients are vitamins and minerals that our body needs in small amounts, but they are absolutely essential for:
- Energy production
- Brain function
- Immune strength
- Bone health
- Hormone balance
We can’t make most of them ourselves — we have to get them from food.

TWO MAIN TYPES OF MICRONUTRIENTS
1. Vitamins
– The Helpers
They support your body in using energy, building tissues, and staying healthy.
Vitamins are of two types:
a. Fat-Soluble Vitamins (stored in body fat)
- Vitamin A – Good for vision and skin (found in carrots, sweet potatoes)
- Vitamin D – Strong bones and immunity (sunlight, eggs, mushrooms)
- Vitamin E – Protects cells (nuts, seeds, spinach)
- Vitamin K – Helps blood clotting (green leafy vegetables)
b. Water-Soluble Vitamins (not stored – need daily)
- Vitamin C – Immunity booster (citrus fruits, amla)
- Vitamin B-complex – Helps energy and nerve health (whole grains, dairy, leafy greens)
2. Minerals
– The Builders
They help build bones, teeth, and carry out key functions like muscle movement and nerve signals.
Here are the most important ones:
- Iron – Carries oxygen (found in spinach, jaggery, lentils)
- Calcium – Builds strong bones and teeth (milk, ragi, tofu)
- Zinc – Boosts immunity and heals wounds (pumpkin seeds, nuts)
- Magnesium – Supports muscles and sleep (banana, dark chocolate)
- Iodine – Keeps thyroid working well (iodized salt, seaweed)
Why Are Micronutrients Important?
Even a tiny deficiency can lead to:
- Weak immunity
- Tiredness and low energy
- Poor growth in children
- Hair fall and skin problems
- Difficulty in concentrating
How to Get Enough Micronutrients?
Simple rule: Eat a rainbow every day!
- Include different colored vegetables and fruits
- Eat whole grains, nuts, seeds, and dairy
- Don’t overcook – it kills vitamins
- Get sunlight for Vitamin D
Final Thought
You don’t need supplements unless a doctor suggests it. A balanced, colorful plate is enough to power your body with all the micronutrients it needs.
Hi, I’m Sonita — the voice behind Healthy Living Hub. I share simple, science-backed tips to live a healthier, more balanced life — one mindful choice at a time.
“I believe real health comes from small, consistent habits — not perfection.”